Unveiling Raman Company Iran: Navigating Sanctions And Innovation
Operating in the intricate and often challenging landscape of Iran's economy requires a unique blend of resilience, strategic foresight, and a commitment to domestic innovation. In this complex environment, the Raman Company Iran stands out as an entity that not only navigates the stringent international sanctions but also contributes significantly to the nation's industrial and technological capabilities. This article delves into the operational facets, challenges, and remarkable achievements of Raman Company, offering a comprehensive look at how it thrives amidst adversity.
From its strategic location in Tehran to its involvement in critical infrastructure projects and the manufacturing of advanced scientific instruments, Raman Company embodies the spirit of self-sufficiency. Despite being subjected to international sanctions, its story is one of continuous development and a testament to the ingenuity found within the Iranian industrial sector. Join us as we explore the multifaceted identity of this intriguing company.
Table of Contents
- The Core Identity of Raman Company Iran
- Raman Company and the Shadow of Sanctions
- Innovation Amidst Adversity: Raman's Product Prowess
- Raman Company Iran's Footprint in Infrastructure and Energy
- Operational Landscape: Addresses and Affiliations
- Overcoming Challenges: A Case Study from Iran
- The Broader Economic Context for Raman Company Iran
- Future Outlook for Raman Company Iran
The Core Identity of Raman Company Iran
At its heart, the Raman Company Iran is an industrial and technological entity with a diversified portfolio, operating from its base in Tehran. Known interchangeably as "Raman Co." or "Raman Industry Company," its identity is rooted in its contribution to various sectors, from advanced scientific instrument manufacturing to large-scale infrastructure projects. The company's primary operational base is strategically located in Tehran, Iran, with an address specified as "29, Daman Afshar St., after Mirdamad Intersection Africa Boulevard Southbound, Tehran, Iran." This central location in the bustling capital city places it at the nexus of Iran's economic and industrial activities, facilitating its various ventures.
- Israels Attack On Iran
- Us Launches Strikes On Iran Backed Houthi Targets In Yemen
- War On Iran
- Iran Air Defense
- Iran Location
The company's existence and operations highlight a significant aspect of Iran's domestic industry: the drive towards self-reliance and technological advancement, particularly in areas where international access might be restricted. While specific details about its founding or early history are not widely publicized, its current activities suggest a well-established presence and a clear focus on high-value industrial and scientific contributions. The very nature of its specialized products, such as the Raman microscope, points to a commitment to sophisticated engineering and research and development.
Raman Company and the Shadow of Sanctions
Perhaps the most defining characteristic of Raman Company Iran, from an international perspective, is its status as a sanctioned entity. The company is explicitly stated to be "subject to sanctions" and is "sanctioned on 1 list(s)." This designation carries significant implications for its operations, international partnerships, and access to global markets. Understanding the root cause of these sanctions is crucial to grasping the unique challenges and operational strategies employed by Raman Company.
Understanding the Bonyad Mostazafan Connection
The primary reason cited for Raman Company's sanctioned status is its ownership or control, "directly or indirectly, by Bonyad Mostazafan." Bonyad Mostazafan, also known as the "Islamic Revolution Mostazafan Foundation," is a powerful and influential economic conglomerate in Iran. Established after the 1979 Islamic Revolution, it was initially tasked with managing confiscated assets and providing aid to the poor and disadvantaged. Over the decades, it has grown into a vast economic empire with interests across numerous sectors, including finance, construction, energy, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Entities associated with Bonyad Mostazafan often find themselves targeted by international sanctions, particularly those imposed by the United States and other Western nations. These sanctions are typically aimed at limiting the financial resources and operational capabilities of organizations perceived to be linked to the Iranian government or its revolutionary institutions. The specific sanction code "13876" associated with Raman Company's connection to Bonyad Mostazafan underscores the official nature of this designation, indicating that it falls under specific regulatory frameworks designed to restrict such entities.
Implications of Being Sanctioned
Being "subject to sanctions" means that Raman Company Iran faces significant barriers to conducting international business. These implications can include, but are not limited to, restrictions on financial transactions, limitations on importing or exporting certain goods and technologies, difficulty in accessing international banking systems, and a general reluctance from foreign companies to engage in partnerships or trade. For a company involved in manufacturing advanced devices and undertaking large-scale projects, these restrictions pose immense challenges to sourcing components, acquiring cutting-edge technology, and expanding into global markets.
The impact of sanctions often necessitates a shift towards greater self-reliance and domestic production. Companies like Raman must innovate internally to overcome supply chain disruptions and technological gaps that would otherwise be filled by international collaboration. This often leads to the development of indigenous expertise and manufacturing capabilities, fostering a more robust domestic industrial base, even if it comes at the cost of slower growth or higher initial investment compared to a fully open market environment.
Innovation Amidst Adversity: Raman's Product Prowess
Despite the formidable challenges posed by sanctions, Raman Company Iran has demonstrated remarkable innovation, particularly in the field of scientific instrumentation. A standout example of its technological capability is the "Raman microscope manufactured by the company." This highly specialized device is critical in various scientific disciplines, including materials science, chemistry, biology, and pharmaceuticals, for non-destructive chemical analysis and imaging.
The data explicitly states that this device "can also compete well with foreign samples." This is a significant claim, highlighting the quality, performance, and technological sophistication of Raman's indigenous manufacturing. In a market where "a number of foreign companies are the main manufacturers of the device," Raman's ability to produce a competitive product underscores its commitment to high standards and its capacity for advanced engineering. This competitiveness is not merely about functionality but also about precision, reliability, and potentially cost-effectiveness within the domestic market, providing a viable alternative to imported instruments that might be difficult to acquire due to sanctions.
Developing and manufacturing such a complex instrument domestically requires substantial investment in research and development, skilled labor, and specialized infrastructure. It reflects a strategic decision by Raman Company to focus on high-tech, value-added products that serve critical scientific and industrial needs within Iran, thereby reducing reliance on external suppliers and bolstering national scientific capabilities.
Raman Company Iran's Footprint in Infrastructure and Energy
Beyond its ventures in scientific instrumentation, Raman Company Iran also plays a role in the nation's critical infrastructure and energy sectors. The data confirms that "Raman industry company has been involved in a project for establishment of a CHP plant in Iran." CHP, or Combined Heat and Power, plants are highly efficient facilities that simultaneously generate electricity and useful heat from a single fuel source. Their establishment is crucial for improving energy efficiency, reducing carbon emissions, and ensuring reliable power and heating supply for industrial or urban areas.
Involvement in such a project signifies Raman Company's capability to undertake large-scale engineering and construction endeavors. It positions the company not just as a manufacturer of specialized equipment but also as a contributor to national energy security and sustainable development. The phrase "Projekty wykonane" (Projects completed) from the provided data, alongside mentions of "roads and urban development" news, further suggests a broader engagement in infrastructure-related activities. While the exact scope of these projects is not detailed, it indicates Raman's versatility and its capacity to contribute to diverse facets of Iran's development agenda, from high-tech manufacturing to essential utilities.
This dual focus on advanced technology and vital infrastructure projects highlights a strategic approach to growth. By diversifying its operations, Raman Company mitigates risks associated with over-reliance on a single sector and maximizes its contribution to Iran's self-sufficiency efforts, particularly under the constraints of international sanctions.
Operational Landscape: Addresses and Affiliations
The operational footprint of Raman Company Iran extends across key locations in Tehran, reflecting its strategic positioning within the country's economic hub. Understanding these addresses and potential affiliations provides further insight into its operational network and strategic relationships.
Strategic Locations in Tehran
The primary address for Raman Company is clearly stated as "29, Daman Afshar St., after Mirdamad Intersection Africa Boulevard Southbound, Tehran, Iran." This address is further confirmed by its Persian equivalent: "آدرس: تهران - بلوار آفریقا(شمال به جنوب) - بعد از تقاطع میرداماد - خیابان دامن افشار - پلاک 29 طبقه چهارم" (Address: Tehran - Africa Boulevard (North to South) - After Mirdamad Intersection - Daman Afshar Street - No. 29, Fourth Floor). The mention of "Africa Boulevard" (now often referred to as Nelson Mandela Boulevard) signifies a prominent and well-known commercial area in Tehran, suggesting a professional and accessible corporate presence.
Additionally, another address, "No.5, Westarmagan St, Africa Blvd, Tehran, Iran," is provided. While it's unclear if this is a secondary office, a manufacturing facility, or a different operational unit, its proximity to the primary address (both on or near Africa Boulevard) indicates a concentrated presence in a key commercial district. Having multiple operational points within a central area can facilitate logistics, client meetings, and access to a skilled workforce, all vital for a company involved in both manufacturing and project management.
Potential Affiliations and Neighboring Entities
The provided data also mentions "PISHRO IRAN FINANCIAL AND INVESTMENT COMPANY" (also known by various aliases including PISHRO IRAN CO. and SHERKAT MALI OOSARMAYEH GOZARI PISHROOIRAN), with an address at "Vanak Square - After Mirdamad Intersection - Ghobadian St." The proximity of Pishro Iran Financial and Investment Company to Raman Company's location (both near Mirdamad Intersection and Africa Boulevard/Vanak Square area) suggests a potential, albeit unconfirmed, business relationship or at least a shared commercial ecosystem. Financial and investment companies often play a crucial role in funding industrial projects, and given Raman's involvement in a CHP plant, such a connection would not be surprising, especially within the network of companies possibly linked to Bonyad Mostazafan.
While the data also listed other seemingly unrelated companies like "2b2 development company ltd" and "Guangzhou hongwang plastic products factory," these appear to be noise in the dataset and do not directly relate to the core operations or identity of Raman Company Iran. The focus remains on Raman's defined activities and its confirmed affiliations.
Overcoming Challenges: A Case Study from Iran
The narrative of Raman Company Iran serves as a compelling case study in corporate resilience and strategic adaptation in the face of severe external pressures. Operating under the burden of international sanctions, particularly those linked to its indirect control by Bonyad Mostazafan, forces Raman to devise innovative solutions for its survival and growth. This involves a multi-pronged approach that emphasizes domestic capabilities, strategic partnerships within Iran, and a relentless pursuit of technological independence.
Firstly, the ability to manufacture a "Raman microscope" that "can also compete well with foreign samples" is a direct outcome of this adaptive strategy. Instead of relying on imported technology or components that are difficult to procure, Raman invests in its own research and development, fostering local expertise. This not only ensures the continuity of its product lines but also contributes to Iran's overall scientific and industrial self-sufficiency. This internal innovation helps mitigate the impact of disrupted supply chains and limited access to global technological advancements.
Secondly, involvement in significant domestic projects, such as the "establishment of a CHP plant," showcases Raman's commitment to contributing to national development. These projects are crucial for Iran's energy infrastructure and urban development, providing a consistent demand for Raman's engineering and project management capabilities. By focusing on essential national needs, Raman secures its operational viability and reinforces its strategic importance within the Iranian economy, thereby navigating the limitations imposed by sanctions.
The "critical error occurred" message, while seemingly a technical glitch in the provided data, might also metaphorically represent the constant operational hurdles faced by companies in sanctioned environments. Yet, the subsequent mention of "projects completed" and "latest news and articles on roads and urban development" implies that despite these challenges, Raman Company continues to deliver and maintain a public profile of active engagement and successful execution. This continuous delivery, even under duress, is a hallmark of resilient organizations.
The Broader Economic Context for Raman Company Iran
The operational environment for Raman Company Iran is inextricably linked to the broader economic and geopolitical realities of the Islamic Republic. Iran's economy, characterized by its significant oil and gas reserves, has long been subject to international pressures, leading to periods of isolation and a strong emphasis on a "resistance economy." This economic philosophy prioritizes domestic production, diversification, and resilience against external shocks, particularly sanctions.
In this context, companies like Raman play a vital role. By developing indigenous technologies, such as the Raman microscope, they reduce Iran's dependence on foreign imports, thereby conserving foreign currency and fostering local job creation. Their participation in large-scale infrastructure projects, like CHP plants, directly contributes to national self-sufficiency in critical sectors like energy. This aligns perfectly with the national economic strategy, making such companies integral to the country's long-term sustainability goals.
Furthermore, the connection to Bonyad Mostazafan, while a reason for sanctions, also places Raman within a powerful domestic economic network. This affiliation can provide access to internal funding, resources, and large-scale government-backed projects, which might otherwise be inaccessible to smaller, independent entities. This internal support system becomes even more crucial when international financial avenues are blocked. The dynamic between being sanctioned internationally and being integrated into a powerful domestic conglomerate creates a unique operational paradox for Raman Company, allowing it to persist and even thrive in a challenging environment.
Future Outlook for Raman Company Iran
The future trajectory of Raman Company Iran will undoubtedly remain influenced by the evolving geopolitical landscape and the persistence of international sanctions. However, based on its demonstrated capabilities and strategic focus, several aspects of its future outlook can be inferred. The company's continued investment in high-tech manufacturing, exemplified by its competitive Raman microscope, suggests a sustained commitment to innovation and technological leadership within Iran. This focus on advanced instrumentation will likely continue to serve the domestic scientific and industrial sectors, which constantly require sophisticated analytical tools.
Furthermore, Raman's engagement in critical infrastructure projects, such as CHP plants, indicates its ongoing role in national development. As Iran continues to modernize its energy sector and urban infrastructure, companies with proven capabilities in these areas will remain essential. This dual focus provides a stable foundation for growth, allowing Raman to leverage its engineering expertise across different high-demand sectors.
While international expansion remains challenging due to sanctions, Raman Company's success in competing with "foreign samples" domestically could, in a hypothetical future where sanctions are eased, position it for broader regional or even global market entry. For now, its resilience and strategic adaptation within the Iranian market serve as a powerful testament to its enduring operational capacity and its contribution to Iran's self-reliant economic model. The company's journey underscores the intricate balance between geopolitical pressures and the persistent drive for industrial and technological advancement.
Conclusion
- What Is Capital City Of Iran
- Saudi Arabia Conflict With Iran
- Biden Response To Iran
- Railroad In Iran
- Darband Tehran Iran
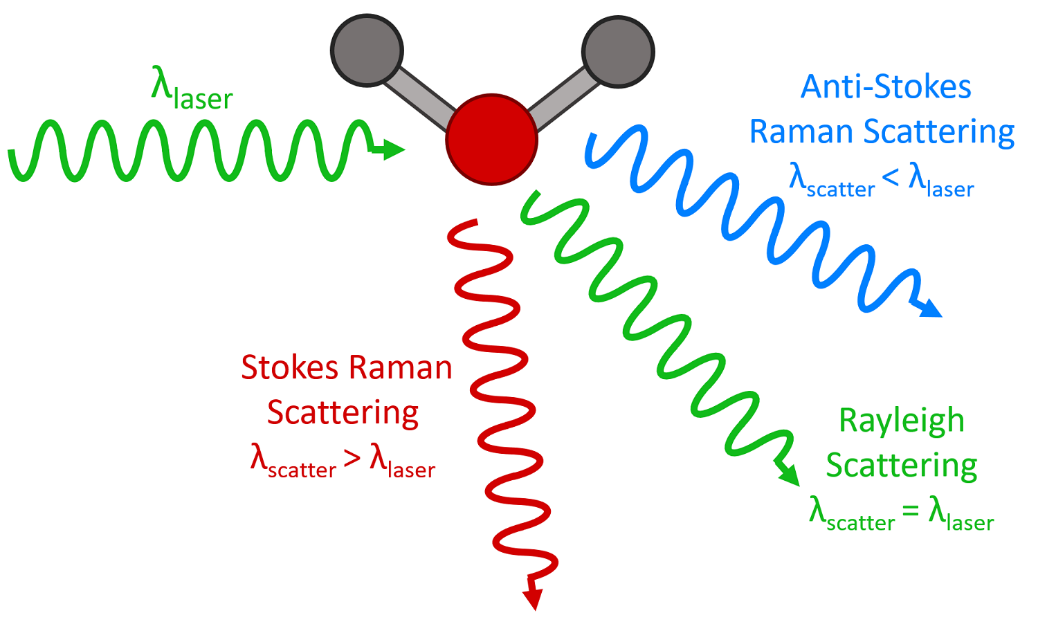
What is Raman Spectroscopy? | Raman Spectroscopy Principle

What is Raman Imaging? | JASCO
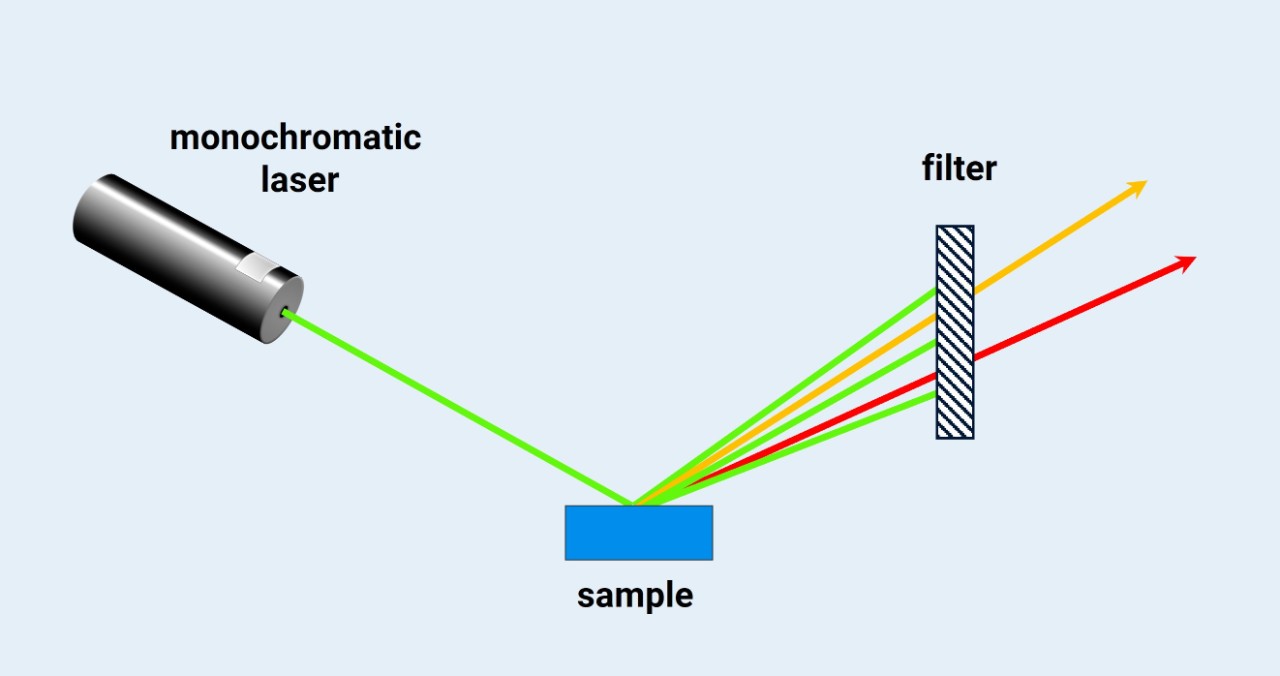
Raman Spectrometer Optics Explained | Bruker